In designing our custom websites, we pay particular attention to SEO. Unlike most of our competitors, we include this service in all our projects. In this article we explain what SEO is, how it differs from SEA and why it is essential to take it into account from the start of the web project.
In this article we explain what SEO is, how it differs from SEA and why it is essential to take it into account from the start of the web project.

When a company wants a new website, it rightly thinks that it is a showcase for its products and services. It is therefore well understood that the site must be visually attractive, clear to the user and that the presentation of its content must be exemplary. But all this implies that the user, customer or future customer, is already on the site.
The first question that should be asked is "how will they get to my site"? Generally, the answer is: "they will find my site on Google"!
Did you know that there are currently 1.93 billion websites online in the world? Moreover, it is admitted that only 4.8% of Internet users visit the second page of the results of the famous search engine.
So for your potential customer to come to your new website, it has to stand out enough to be in the top 10 results of Google, in your geographical area, on the most important search terms for your business! Quite a challenge, isn't it?
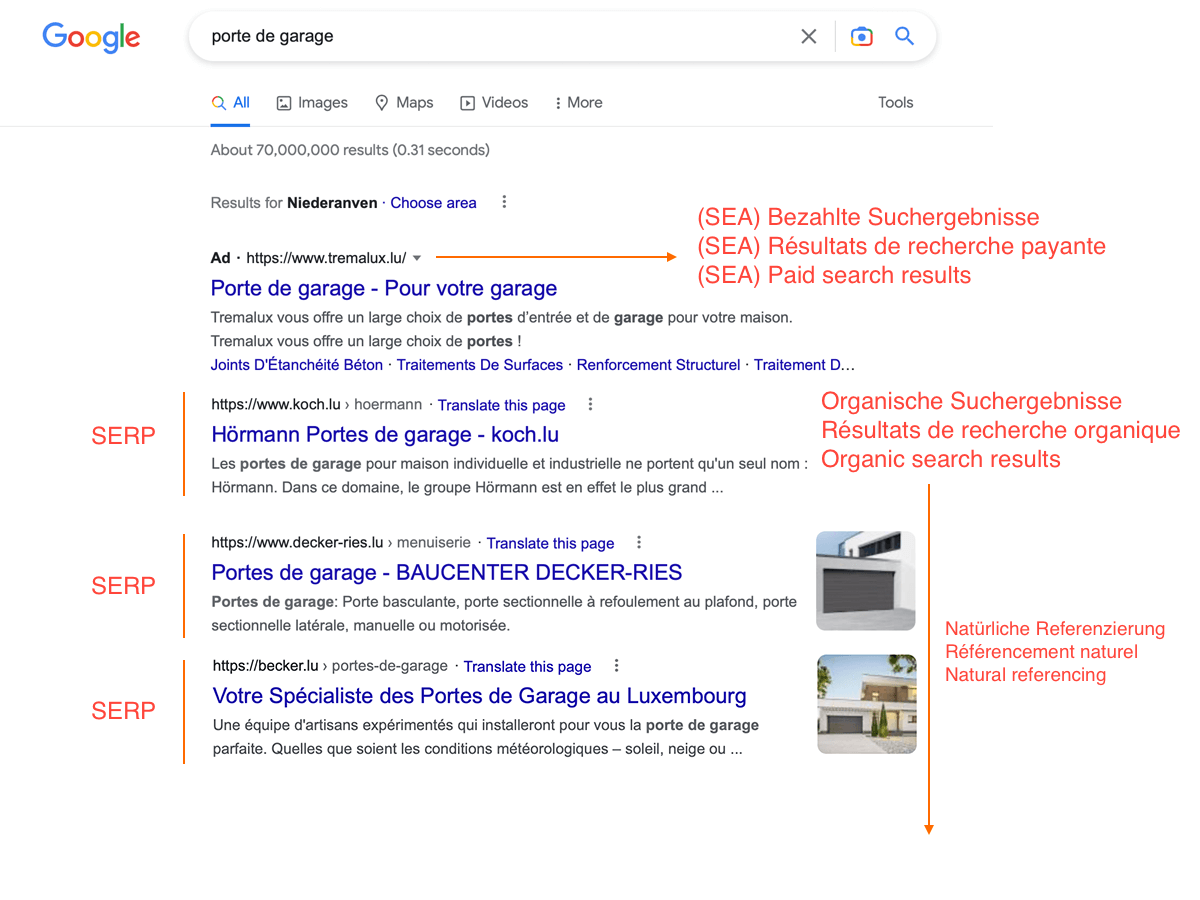
There are two ways to get your site to reach this holy grail: SEO and SEA. We will see here what differentiates them both and why SEO must be thought of from the design of the website.
What is SEO and how does it differ from SEA?
SEO stands for "Search Engine Optimization". It is therefore about techniques that promote organic, natural ranking in search engines like Google.
SEA, on the other hand, means "Search Engine Advertising". It is therefore a paid referencing based on bids on keywords. It has the advantage of positioning the site directly at the top of the results in return for payment.
SEO and SEA are independent of each other and do not occupy the same places on the results page. It should be noted, however, that since the SEA takes into account the quality of the page to calculate part of the bid, a page that is well optimised in SEO and therefore more qualitative will be favourable for the SEA. The link between the two ends there.
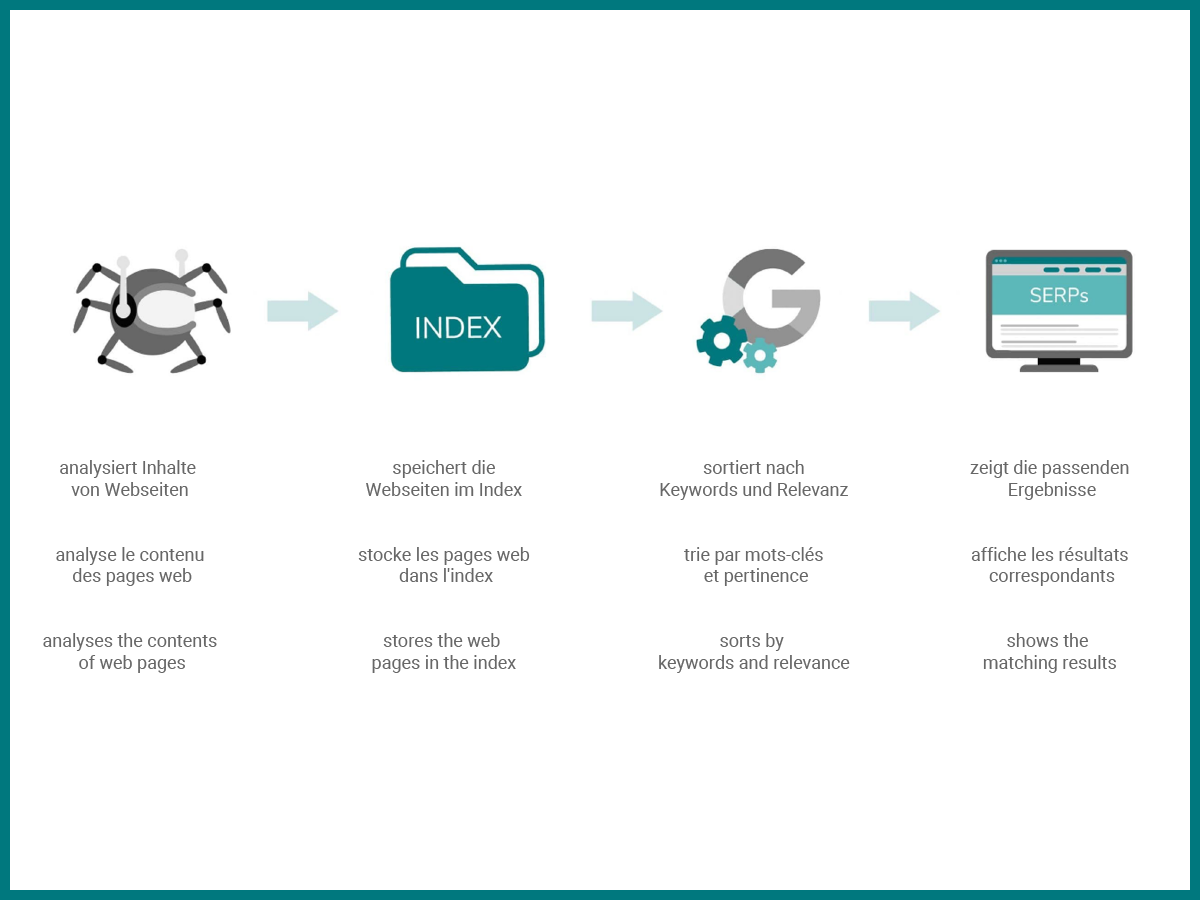
How do search engines work?
Search engine bots, such as the one from Google, are constantly crawling the World Wide Web for new content to feed on. They absorb everything they find and classify it in their index. To find their way through this immense library, they use a very powerful algorithm. This algorithm is kept secret, is constantly evolving and has more than 280 criteria.
When a user enters a specific keyword into the search engine, Google extracts the pages they deem most relevant from its index and presents them to the user in the search results (SERP).
The more relevant it deems the page to be to the user's query, the better it will be positioned. Google's focus is always on delivering the best possible result to the user.
How does it assess this relevance? What are the essential criteria it takes into account? Answering these questions is the key to our work in SEO.
The 5 ranking factors
No one outside of Google's engineers knows all the factors of the algorithm, but it is commonly accepted that 5 factors are of primary importance. These are the basics in terms of website optimisation. If these are missing, it becomes increasingly difficult to be well ranked in the search engine.
Here they are in order of importance:
- Content and mainly textual content: The quality of the content for the user, the quantity of text, the presence of keywords and the degree of interest of the page for the visitor.
- The technical structure: Is a website cleanly constructed? Is its code easily and quickly readable by the robot? Is the page structured and does it include the right On-Page tags? Is the server speed and page load speed high enough? You understand here that this 2nd point must be addressed as early as the design of your custom website by the developer himself.
- User signals: Google recognises, for example, whether a user is satisfied with the search result he has clicked on. This is the so-called "user experience".
- Backlinks: Google considers that the more external links a site has pointing to it, the more notoriety and therefore interest it has. Be careful here, we are talking about qualitative links, i.e. links from quality websites that are relevant to the content of your site. A link from a weather directory for your site that sells garage doors will be of little interest.
- Mobile Friendly: For over a year now, Google has been "mobile first", which means that the mobile index takes precedence. Your new site must therefore be well adapted to mobile devices. Does it display correctly on smartphones and tablets? And above all, does it load quickly enough?
This is also an essential point to be addressed at the design stage.

How does SEO work in practice?
A successful SEO strategy generally covers three areas: content, backlinks (Off-Page) and building (On-Page).
The first step in search engine optimisation is to carry out an audit of the current situation. This will allow us to assess the work that needs to be done. We will first make sure that the technical criteria are met and that there are no structural blockages.
Then we will work on the On-Page factors such as tags and content to reinforce, in particular, the presence of relevant keywords. Once all this is in place, the backlinking strategy can be addressed.
We would like to draw your attention to the fact that SEO is a medium/long term job since indexing depends on the goodwill of the search engine and is re-evaluated each time the robot visits the site. The results are only sustainable if search engine optimisation is seen as a long-term support.
The content of the site is valuable and must be regularly renewed in order to satisfy the search intentions of the visitors.

On Page factors
On-Page SEO is the optimization of individual web pages in the hope of achieving higher rankings and increasing quality search engine traffic.
On-Page SEO includes:
- Textual content
- Title tag
- H1, H2, H3 tags
- The meta description tag
- Internal link anchors
- The Alt of images
- Permalinks or URLs
All of them must contain a good proportion of the targeted keywords. But also beware of over-optimisation! Keyword stuffing is penalised by Google in the same way as duplicate content! The content must remain readable, above all, for the human user!
Work on SEO from the design of the site and then go further together
As you can see, for your site to rank well in Google, it is not enough for it to have an aesthetic design and to be pleasant for the user. It must meet a series of technical criteria from the outset. In addition, its content in terms of keywords and their place in the On-Page criteria is one of the keys to SEO.
At Amyma, we are passionate about SEO and we find it normal that it is one of the foundations of our custom web development business.
We will work with you from the audit of your existing site to the ongoing optimisation of your site over the long term.
And if SEO doesn't bring you fast enough results, we manage SEA campaigns for you so that your site is at the top of the results.
Contact us for any SEO, SEA or website creation request





